www.iotatoken.com
Iota
Iota is a brand new and novel micro-transaction cryptotoken optimized for the Internet-of-Things (IoT). Unlike the complex and heavy blockchains of Bitcoin and the like, which were designed with other uses in mind, Iota is created to be as lightweight as possible, hence the name "Iota" with emphasis on the ‘IoT’ part.
The number of connected devices that will permeate our modern landscape in the coming decade is estimated to be 50 billion(!) Each of these are designed to make the world a better and more seamless place for us. Tied to this fantastic promise are of course a ton of obstacles to be overcome, of which one major one is micro-transactions. These connected IoT devices must be able to automatically pay miniscule amounts to one another in a frictionless manner without having to compromise on product design by introducing additional hardware. This is why Iota was conceived.
While it was developed as a solution to scalability issues faced in IoT, the underlying protocol is agnostic and can be applied in any other use-cases that utilize micro-transactions.
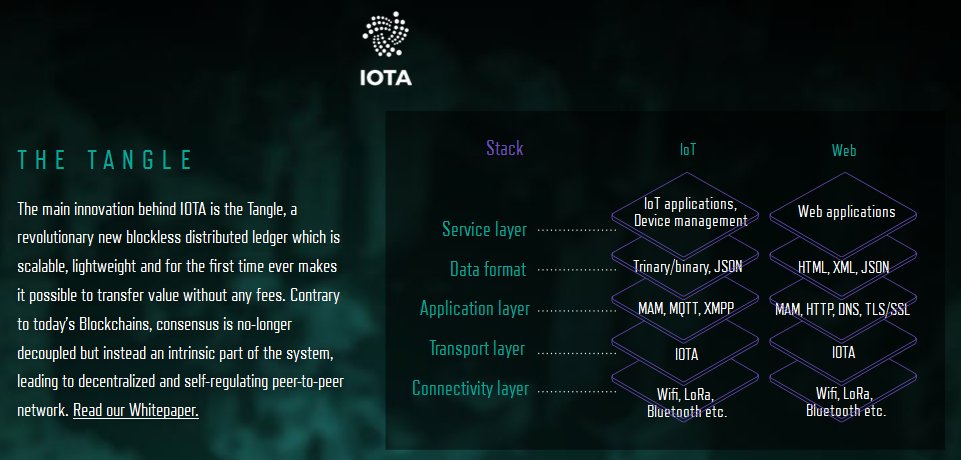
In order to achieve these audacious goals Iota’s design diverged radically from blockchain cryptocurrencies. It still retains the core principle ideas of the distributed consensus blockchain, but in order to be able to scale to the size of the coming Internet-of-Things ecosystem with tens of billions of devices that are connected to each other, it needed to be very lightweight and efficient. This problem is solved by Iota’s core innovation: the tangle.
Tangle
A Tangle is a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG).

Tangle vs Blockchain
Iota’s blockchain solves the following problems of its blockchain cousin:
Centralization of control
As history shows, small miners form big groups to reduce variation of the reward. This leads to concentration of power (computational and political) in hands of few pool operators and gives them ability to apply wide spectrum of policies (filtering, postponing) on certain transactions. Although there are no known cases where pool operators abused their power, there have been several instances where the opportunity were present. This possibility in a monetary system powering a multibillion (in USD) industry is completely unacceptable.
“Obsolete” cryptography
Although large scale quantum computers do not exist yet, future oriented companies have already begun initiating the steps towards quantum-resistant cryptography. From a security point of view it makes perfect sense to assume that hardware capable of cracking classical cryptoalgorithms may appear in the very near future, so preparation is the only defense.
Inability to conduct micropayments
Transaction fees are used to cover miner expenses and mitigate spam-attacks. They also set a threshold on the minimum amount of a payment below which money transfers become inexpedient.
Partition intolerance
Blockchain-based currencies are unable to survive long-sustained partitioning of the network because this may lead to reversal of a large number of transactions. It is also impossible to initiate an intentional partitioning in cases when it is required.
Discrimination of participants
Existing cryptocurrencies are heterogeneous systems with clear separation of roles (transaction issuers, transaction approvers). Such systems create unavoidable discrimination of some of their elements which in turn creates conflicts and makes all elements spend resources on conflict resolution.
Scalability limits
Some cryptocurrencies have hard limits on the maximum transaction rate and this limits cannot be removed in a decentralized manner. A magic number of a limit set before the launch cannot satisfy requirements of a system unless it is set by a person with extraordinary prediction skill. A too low value may hinder growth of the userbase, a too high value may open system to different kinds of attacks.
High requirements for hardware
Bitcoin-derived cryptocurrencies use its original script-based approach which allows implementation of a wide range of use-cases. Other currencies use an approach similar to one used by banks but add extra features. They both substantially raise requirements for hardware because of complex transaction processing logic.
Unlimited data growth
Storing of all state transitions leads to fast growth of data while does not increase stored balance information significantly. This inefficiency cannot be removed even with data pruning technique and high popularity of the currency may lead to its collapse.
Tangle-blockchain interoperability
Iota does not seek to replace the blockchain entirely, it also acts as a supplementation to the current blockchain ecosystem by acting as a oracle for smart contract platforms like Ethereum and Rootstock. Additionally it increases security of blockchains by enabling the ability to include checkpoints for transactions.
special thanks to: Jimmy2011 and Kushti for reviews.
Also worth noting: Sergio_Demian_Lerner's thread about DAG in crypto here: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=1177633.0
http://cointelegraph.com/news/115508/iota-a-blockchain-less-gasp-token-for-the-internet-of-things